DOM
What is Virtual DOM?
The Virtual DOM (VDOM) is an in-memory representation of Real DOM. The representation of a UI is kept in memory and synced with the "real" DOM. It's a step that happens between the render function being called and the displaying of elements on the screen. This entire process is called reconciliation.
How Virtual DOM works?
The Virtual DOM works in three simple steps.
Whenever any underlying data changes, the entire UI is re-rendered in Virtual DOM representation.
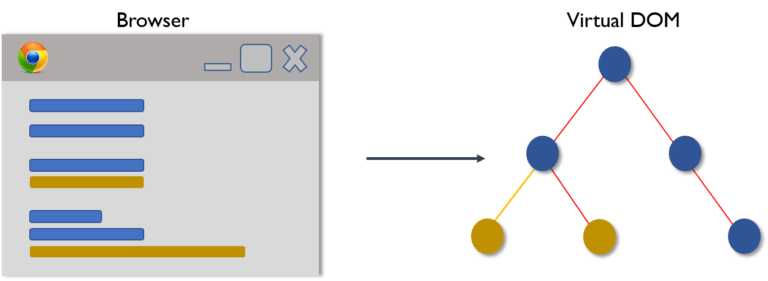
Then the difference between the previous DOM representation and the new one is calculated.
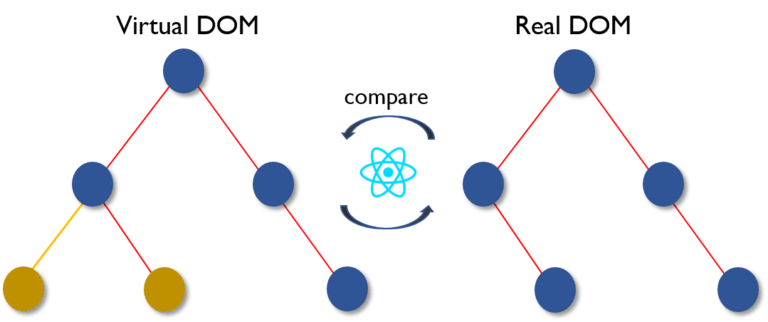
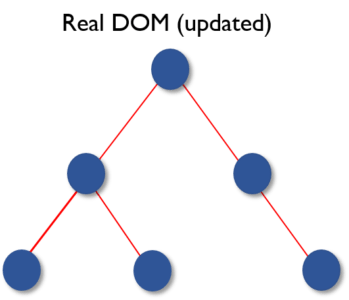
Once the calculations are done, the real DOM will be updated with only the things that have actually changed.
What is the difference between Shadow DOM and Virtual DOM?
The Shadow DOM is a browser technology designed primarily for scoping variables and CSS in web components. The Virtual DOM is a concept implemented by libraries in JavaScript on top of browser APIs.
What is the use of react-dom package?
The react-dom package provides DOM-specific methods that can be used at the top level of your app. Most of the components are not required to use this module. Some of the methods of this package are:
render()hydrate()unmountComponentAtNode()findDOMNode()createPortal()
What is the difference between React and ReactDOM?
The react package contains React.createElement(), React.Component, React.Children, and other helpers related to elements and component classes. You can think of these as the isomorphic or universal helpers that you need to build components. The react-dom package contains ReactDOM.render(), and in react-dom/server we have server-side rendering support with ReactDOMServer.renderToString() and ReactDOMServer.renderToStaticMarkup().
Why ReactDOM is separated from React?
The React team worked on extracting all DOM-related features into a separate library called ReactDOM. React v0.14 is the first release in which the libraries are split. By looking at some of the packages, react-native, react-art, react-canvas, and react-three, it has become clear that the beauty and essence of React has nothing to do with browsers or the DOM.
To build more environments that React can render to, React team planned to split the main React package into two: react and react-dom. This paves the way to writing components that can be shared between the web version of React and React Native.
What is the purpose of render method of react-dom?
This method is used to render a React element into the DOM in the supplied container and return a reference to the component. If the React element was previously rendered into container, it will perform an update on it and only mutate the DOM as necessary to reflect the latest changes.
If the optional callback is provided, it will be executed after the component is rendered or updated.
What is ReactDOMServer?
The ReactDOMServer object enables you to render components to static markup (typically used on node server). This object is mainly used for server-side rendering (SSR). The following methods can be used in both the server and browser environments:
renderToString()renderToStaticMarkup()
For example, you generally run a Node-based web server like Express, Hapi, or Koa, and you call renderToString to render your root component to a string, which you then send as response.
Are custom DOM attributes supported in React v16?
Yes. In the past, React used to ignore unknown DOM attributes. If you wrote JSX with an attribute that React doesn't recognize, React would just skip it.
For example, let's take a look at the below attribute:
Would render an empty div to the DOM with React v15:
In React v16 any unknown attributes will end up in the DOM:
This is useful for supplying browser-specific non-standard attributes, trying new DOM APIs, and integrating with opinionated third-party libraries.